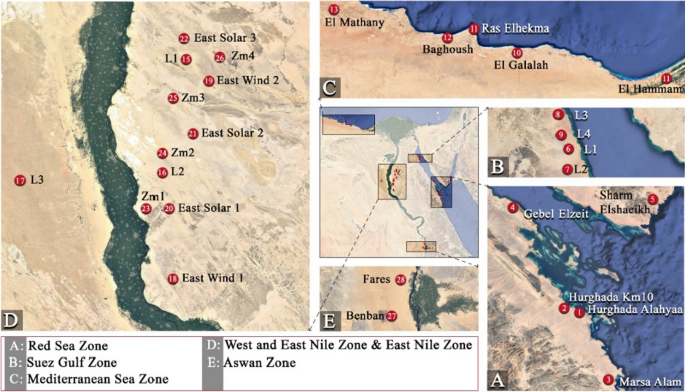
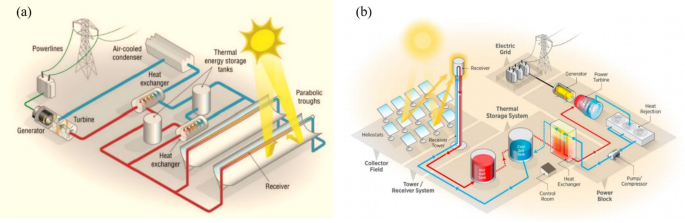
Introduction
- Annual Direct Normal Irradiation (DNI) should be greater than 1900kWh/m2(Zhao et al.2009).
- Flat land area with an overall slope of less than 1–3% (Yang et al.2010), as the intensity of solar radiation is essentially controlled by the ground slope at a certain location (Allen et al.2006). Due to various parameterssuch as self-shadowing and shading cast by surrounding terrain, the amount of radiation intercepted by the collectors is significantly reduced. As a result, land with a steeper slope has an impact on solar plant productivity.
- The wind speed should be less than 15.64m/s in order to decrease the stresses applied to the support structure of the solar collector assembly (Shahrukh Saleem and ul Asar2021).
- Availability of accessible grid connections if the CSP project is not designed to fulfill a specific local (site) demand for industrial applications.
- Availability of water resources, as the large amount of water consumed in the cooling towers is one of the disadvantages of CSP for power generation.
- The availability of good transportation facilities is a socio-economic aspect that should be considered in developing remote areas where CSP projects are usually built.
- Consideration of protected areas, wildlife traffic, and agriculture.
- Availability of a backup fuel supply.
Concentrated solar power (CSP) technologies
Multi-criteria decision making for optimum site and technology selection
Materials and methods
Environmental data
Technical data
Financial data
Economic data
Model validation
Parabolic trough collector mathematical model
ηPTC=0.75−4.5×10−5(Tcol−Tamb)−0.039(Tcol−TambG)−3×10−4×G(Tcol−TambG)2
(1)
Q=Afield×ηPTC×G
(2)
APTC=LPTC×(Wcol−Denv)
(3)
Nloop=m.colm.hyd
(4)
Aloop=APTCNloop
(5)
Wloop=AloopLm
(6)
NPTCs=APTCLm×(Wcol−Denv)
(7)
Ptloss=Nloop×ΔPloop
(8)
Central solar tower mathematical model
ηfield=ηrefl×ηatt×ηcos×ηsh&bl
(9)
Q=Afield×ηfield×G
(10)
Trec=(To−Tiεcav)+Ti
(11)
Validation results
Results and discussion
Conclusion and prospects
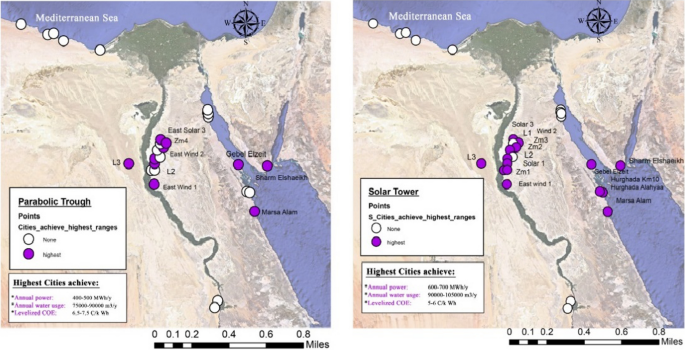
- The solar tower configuration requires 25% more land than the parabolic trough configuration. This increase in collector area elevated the solar tower’s net capital cost by 15% above the parabolic trough.
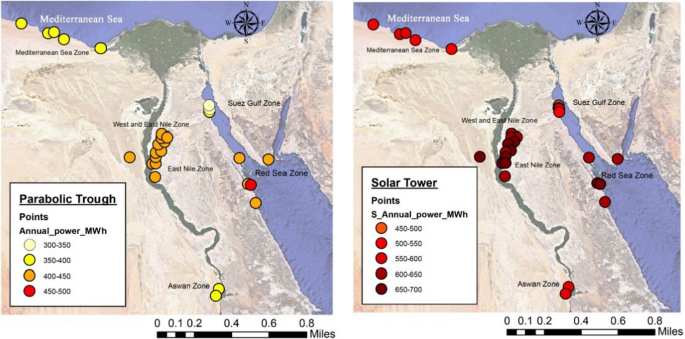
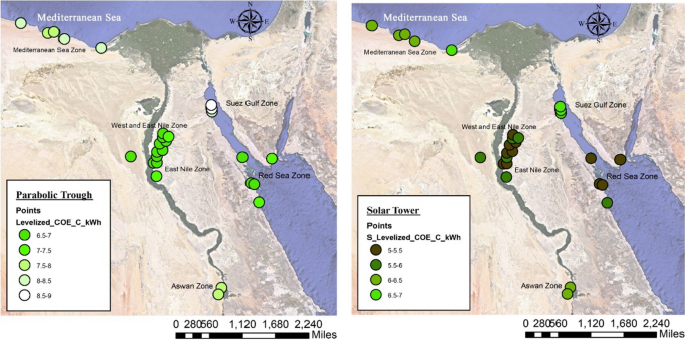
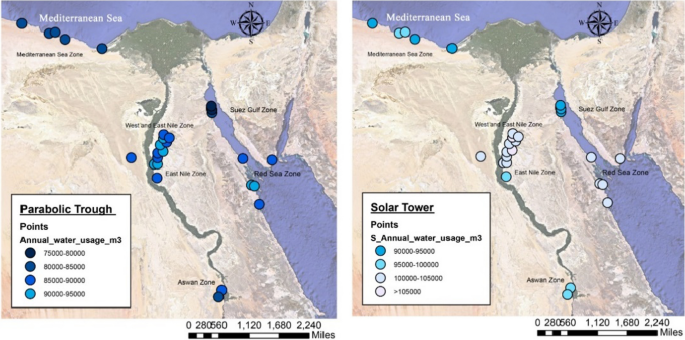
- For both technologies, plants in the northern zones (Mediterranean and Suez Gulf) consume less water than those in the central, eastern, and southern zones.
- Plants implemented in the central zone (Nile zones) generate more annual electricity output than plants in the southern region (Aswan), eastern zone (Red Sea), and northern zone (Mediterranean Sea and Suez Gulf), respectively.
- According to the parametric analysis, the eastern zones have been shown to be an advantageous area for implementing both indicated technologies.
Availability of data and materials
Abbreviations
- A:
- Area, m2
- G:
- Solar irradiance, W/m2
- N:
- Number
- P:
- Pressure, bar
- Q:
- Thermal power, W
- T:
- Temperature, °C
- W:
- Width, m
- CSP:
- Concentrated solar power
- CST:
- Central solar tower
- DNI:
- Direct normal irradiation
- EFLSH:
- Equivalent full load storage hours
- EPC:
- Engineering, procurement, and construction
- GHG:
- Greenhouse gas
- GHI:
- Global horizontal irradiance
- GIS:
- Geographic information system
- HTF:
- Heat transfer fluid
- IRR:
- Internal rate of return
- LCOE:
- Levelized cost of energy
- LEC:
- Levelized energy cost
- LFR:
- Linear Fresnel reflector
- MACRS:
- Modified accelerated cost recovery system
- MENA:
- Middle East and North Africa
- NREA:
- New and renewable energy authority
- PTC:
- Parabolic trough collector
- SAM:
- Sam advisory model
- SM:
- Solar multiple
- amb:
- Ambient
- att:
- Atmospheric attenuation factor
- cav:
- Cavity
- col:
- Collector
- cos:
- Cosine factor
- e:
- Electricity
- env:
- Glass envelope
- hyd:
- Hydraulic
- i:
- Inlet
- m:
- Module
- o:
- Outlet
- refl:
- Mirror reflectivity factor
- sh&bl:
- Shadowing and blocking factor
- t:
- Thermal
- tloss:
- Total loss
- η:
- Efficiency, %
- ε:
- Effectiveness